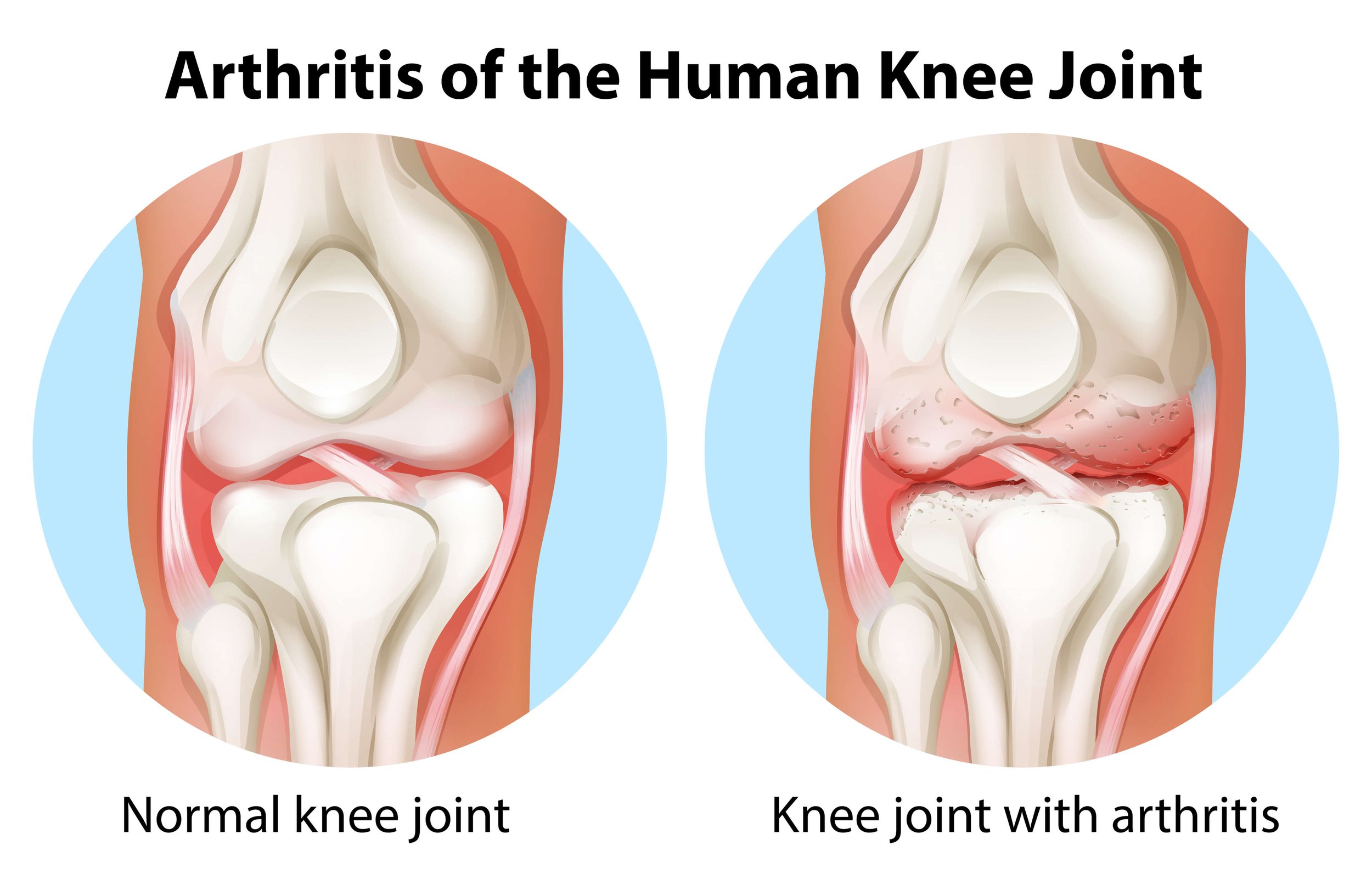
Knee Osteoarthritis
Overview
The most common form of arthritis.
Knee osteoarthritis wears away your cartilage (the cushioning between the three bones of your knee joint), causing your bones to rub against each other.
Symptoms include knee pain and stiffness, popping/clicking sound, swelling around the joint.
Manage pain by maintaining a healthy weight and exercising.
Geniculate artery embolization and platelet-rich fibrin injections can help manage pain, too.

How common is knee arthritis?
Knee arthritis is very common. In fact, 46% of people will develop it during their lifetimes. This makes it the most common form of osteoarthritis.
What are the causes of knee arthritis?
The most common cause is age-related wear and tear of the cartilage. Other causes include injury to the knee joint, overuse of the joint, and obesity.
What does arthritis in the knee feel like?
Experiencing arthritis in the knee can be quite uncomfortable. Symptoms can include a dull ache, pain, stiffness, swelling that’s warm to the touch, creaking, clicking, grinding, or snapping that causes difficulty in moving the joint, especially during cold weather.
In more severe cases where the knee joint has significantly deteriorated, even walking and moving can cause pain and discomfort. Pain can be constant and lead to disturbed sleep, fatigue, and depression.
How is knee arthritis diagnosed?
An interventional radiologist can help to diagnose knee arthritis with imaging tests such as x-rays, MRIs, and CT scans. These tests can help to identify the severity of the condition and determine the best course of treatment.
What happens if knee arthritis is left untreated?
If ignored, the situation gets worse. Knee arthritis affects quality of life and overall health.
What are the risk factors of knee arthritis?
The knee is one of the most common joints affected by osteoarthritis, and there are several risk factors that can increase the likelihood of developing this condition:
Age (the most significant factor because it’s more common in older adults)
Obesity
Joint injury
Repetitive stress on the joints
How you can manage knee arthritis pain
Although there is no cure to knee arthritis, there are ways to manage pain.
Maintain a healthy weight.
Change your diet, reduce weight, and exercise. Extra weight causes stress to weight-bearing bones, including the knees, which can worsen knee arthritis.
Wear knee braces and apply ice.
Knee braces help stabilize the knee joint.
What is treatment like for knee arthritis?
Genicular artery embolization
A non-surgical procedure that is used to treat pain and inflammation in the knee.
Candidates for geniculate artery embolization include those who have experienced pain and inflammation for more than six months and have not responded to other conservative treatments. Learn more.
Platelet-rich fibrin injections
This procedure involves extracting a small amount of blood, separating its components to obtain platelet rich fibrin, and then injecting it directly into the knee joint to help reduce inflammation and pain while promoting healing. Learn more.